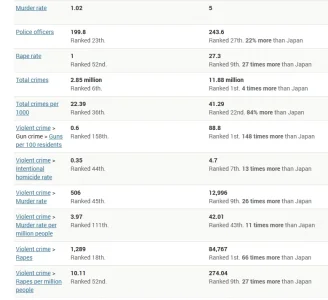
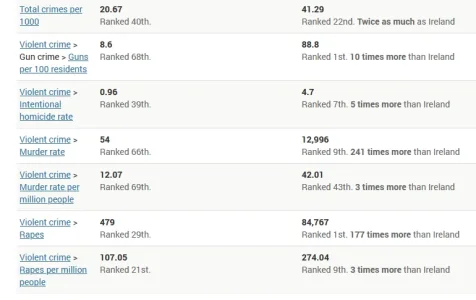
The Regan years was one of the better time periods this country had. He broke the USSR. He used a lot of common sense.....does anyone remember what that was?I’m going to guess you are young enough that you weren’t around for the election of Reagan.
Cheers,
Ian
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Trump will win again
- Thread starter slant
- Start date
More options
Who Replied?Like the rest of the libs, you have no idea. Like the rest of the libs you lower yourself even lower by going to insults rather than dealing with facts.One day you'll become a real boy
Best of luck out there
Few countries have lasted more than 200 years. Because of your fellow libs looking to shit on the US Constitution, we may very well be on the edge of a revolt. Hitler's first step was to take away his countrymen's ability to defend themselves. What does Kammy want to do with firearms? Take away all semi-automatics....better known by libs who don't have a clue what a battle weapon is....as "assault weapons".
I wonder how much we paid for Kammy's new personality...........
LOL. I'll see if I can get copies of the pieces a friend of mine has. She repeats herself using exact phrases used in past speeches. It's hilarious. One of them is "unburdened by what has been". WTF is that? LOL.I have no idea what you mean. That said, the original post demonstrates that JD Vance is a real politician. A charlatan, sell-out, hypocrite, and opportunist.
Which is okay...you don’t get the job without a little malfeasance. And in his case, kissing the ring.
Cheers,
Ian
There isn't a politickcian out there that isn't a hypocrite. If they are so dedicated to their citizens why do they refuse term limits? Power, money, living outside the laws the rest of us have to live by because they are entitled. Chuckyou Schumer has never had a job in his life. A tick since he got out of college, looking down on the rest of us. People are abandoning New York and California.
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
Hitler's first step was to take away his countrymen's ability to defend themselves.
Following Germany's defeat in World War I, the Weimar Republic passed very strict gun control laws in an attempt both to stabilize the country and to comply with the Versailles Treaty of 1919 – laws that in fact required the surrender of all guns to the government. These laws remained in effect until 1928, when the German parliament relaxed gun restrictions and put into effect a strict firearm-licensing scheme. These strict licensing regulations foreshadowed Hitler's rise to power.
If you read the 1938 Nazi gun laws closely and compare them to earlier 1928 Weimar gun legislation – as a straightforward exercise of statutory interpretation – several conclusions become clear. First, with regard to possession and carrying of firearms, the Nazi regime relaxed the gun laws that were in place in Germany at the time the Nazis seized power. Second, the Nazi gun laws of 1938 specifically banned Jewish persons from obtaining a license to manufacture firearms or ammunition. Third, approximately eight months after enacting the 1938 Nazi gun laws, Hitler imposed regulations prohibiting Jewish persons from possessing any dangerous weapons, including firearms. https://scholarship.law.columbia.edu/faculty_scholarship/1327/
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
The Regan years was one of the better time periods this country had. He broke the USSR. He used a lot of common sense.....does anyone remember what that was?
Reagan came to office in 1981 with a mandate to reduce federal spending. In reality, he increased it through the escalating military budget, all the while slashing funds for domestic programs that assisted working class Americans, particularly the poor.
Reagan’s fans give him credit for restoring the nation’s prosperity. But whatever economic growth occurred during the Reagan years only benefited those already well off. The income gap between the rich and everyone else in America widened. Wages for the average worker declined and the nation’s homeownership rate fell. During Reagan’s two terms in the White House, which were boon times for the rich, the poverty rate in cities grew. https://shelterforce.org/2004/05/01/reagans-legacy-homelessness-in-america/
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
niar
Community Member
- MBTI
- intj
It's like they're brainwashed repeating lib news and facts given to them by other libs. They won't discuss. They get angry and start with the insults, going way off track.
Because you feel threatened about an imaginary situation's concequences [libs will take my guns -> unknown entity will be stupid enough to go against the strongest military of the world -> I won't be able to protect myself.]
White we feel threatened about real life shit. [I'm a woman -> trumpers want to take away every reproductive health care choice I have -> this could ruin my life and even get me killed in the case of miscarriage].
The time for discussion with trump bootlickers is over for a lot of people and I don't blame them one bit. It's impossible to have a constructive discussion with a person who solely operates on emotion, and will proritize their fear and hate at the expense and harm of others.
You have to literally use cult deprogramming techniques but that takes a lot of knowledge, patience, and fucks to give.
- MBTI
- ENFP
- Enneagram
- 947 sx/sp
Agreed. 110%. Show me an amygdala pegged in the red, and I’m out.It's impossible to have a constructive discussion with a person who solely operates on emotion, and will proritize their fear and hate at the expense and harm of others.
I’m all out of those.You have to literally use cult deprogramming techniques but that takes a lot of knowledge, patience, and fucks to give.
Seriously, though, that is what it requires, and who has the time, resources, or skills to do that?
There’s a reason the subreddit QAnonCasualties exists.
Cheers,
Ian
Jexocuha
Cave Ghost
- MBTI
- 0x494E
- Enneagram
- 0b100
I've gotta hand it to the Republicans though. From the mouth of the Great Republican George W. Bush himself, they called it "weird" first:
Former U.S. President George W. Bush quote on former U.S. President Donald Trump's inaugural address: "That was some weird shit".
I've gotta hand it to the Republicans though. From the mouth of the Great Republican George W. Bush himself, they called it weird first
Come on man, at least be full circle truthful.
Democrats and Republicans are opposite wings of the same bird. Side choosers remain in the cage they lock themselves in.
Act like you have a choice? How? Every single option is pre selected.
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
The way a two party system works is you have the party in power and the party out of power. Within those parties you have factions vying for dominance. That is how the policy positions of the parties change over time. In the 1800s the Democrats were the party of slavery while the Republicans were fierce advocates of emancipation. In the 1960s, civil rights would not have overcome some hardline Democratic reticence without the aid of some in the Republican party.
More recently the progressive economic policies of Elizabeth Warren (herself a former Republican) and self styled democratic socialist Bernie Sanders were adopted to a large measure by the Bidden administration. These policies were eschewed by policy makers in the Clinton Administration of the 1990s.
There is no doubt however that large business conglomerates continue to hold the most power in the American political environment. Predominated bu the fossil fuel industry which has successfully obscured the immanent danger global warming since the 1970s in the face of the fact that not only will the human caused rise in temperature cause significant hardship to Americans but also that transitioning to non fossil fuels is completely within current level of technology and doing so would make the economy more vibrant.
More recently the progressive economic policies of Elizabeth Warren (herself a former Republican) and self styled democratic socialist Bernie Sanders were adopted to a large measure by the Bidden administration. These policies were eschewed by policy makers in the Clinton Administration of the 1990s.
There is no doubt however that large business conglomerates continue to hold the most power in the American political environment. Predominated bu the fossil fuel industry which has successfully obscured the immanent danger global warming since the 1970s in the face of the fact that not only will the human caused rise in temperature cause significant hardship to Americans but also that transitioning to non fossil fuels is completely within current level of technology and doing so would make the economy more vibrant.
I understand the two party theory. I just don't think that is how things really work. It is effective at keeping the population under control. If they believe that the different parties are keeping the other honest. At this point, I don't. Does the current Senate, Congress and House represent the best America has to pick for these critical law making positions? For me things seem fake and orchestrated now. Example from today.The way a two party system works is you have the party in power and the party out of power. Within those parties you have factions vying for dominance. That is how the policy positions of the parties change over time. In the 1800s the Democrats were the party of slavery while the Republicans were fierce advocates of emancipation. In the 1960s, civil rights would not have overcome some hardline Democratic reticence without the aid of some in the Republican party.
More recently the progressive economic policies of Elizabeth Warren (herself a former Republican) and self styled democratic socialist Bernie Sanders were adopted to a large measure by the Bidden administration. These policies were eschewed by policy makers in the Clinton Administration of the 1990s.
There is no doubt however that large business conglomerates continue to hold the most power in the American political environment. Predominated bu the fossil fuel industry which has successfully obscured the immanent danger global warming since the 1970s in the face of the fact that not only will the human caused rise in temperature cause significant hardship to Americans but also that transitioning to non fossil fuels is completely within current level of technology and doing so would make the economy more vibrant.


These are congress women?
Anyway I'm going to avoid politics.
Do you remember before global warming, that it was supposed to be a coming ice age?
 I think there is a list of new events that is ever growing and developing in a story line fashion. They just ride events it til the wheels fall off or someone says "hey wait a minute?" Then the next thing happens and the last critical scare fades into the mist and is easily forgotten. It feels like that's what happens.
I think there is a list of new events that is ever growing and developing in a story line fashion. They just ride events it til the wheels fall off or someone says "hey wait a minute?" Then the next thing happens and the last critical scare fades into the mist and is easily forgotten. It feels like that's what happens.Now monopoly corps like Vangard and Blackrock are majority share holders in literally everything. Not just companies, but every company in entire industries. Is this not what Bell telephone was broken up for but on a much larger scale?
Fossil fuels vs EV? Neither imo are a good choice vs hydrogen fuel. It's just when people demonstrate that it works and works far better than gas for range and exhaust, they always have car crashes or fall of balconies for some reason.
I understand your points and appreciate the feedback. I just don't think things are as they are presented.
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
@Moranga , it has been observed that changes in the way candidates are legally enabled to raise money for campaigns have lessened the political parties' influence over who becomes a candidate and what they do in office. For many, becoming cultural memes has led to a source of revenue. The argument is that some candidates are driven to making media waves by any means necessary.
Ironically many of those changes in fundraising were initially enacted to limit the influence of money.
I think it is instructive to look at the original progressive movement of the late 1800s which was a reaction of independent businesses that provided professional services against what was referred to as large combinations of business pushing out the independents.
When you look at how the Feds struggle in court in any anti trust litigation against the myriad of lawyers large corporations deploy you get a sense of where the real political power is.
Ironically many of those changes in fundraising were initially enacted to limit the influence of money.
I think it is instructive to look at the original progressive movement of the late 1800s which was a reaction of independent businesses that provided professional services against what was referred to as large combinations of business pushing out the independents.
When you look at how the Feds struggle in court in any anti trust litigation against the myriad of lawyers large corporations deploy you get a sense of where the real political power is.
SlowUpTake
Permanent Fixture
- MBTI
- INFJ
- Enneagram
- ?
I also think that the European religious wars following the dissemination of information stemming from the rise in literacy rates and the establishment of printing presses is an echo of our times